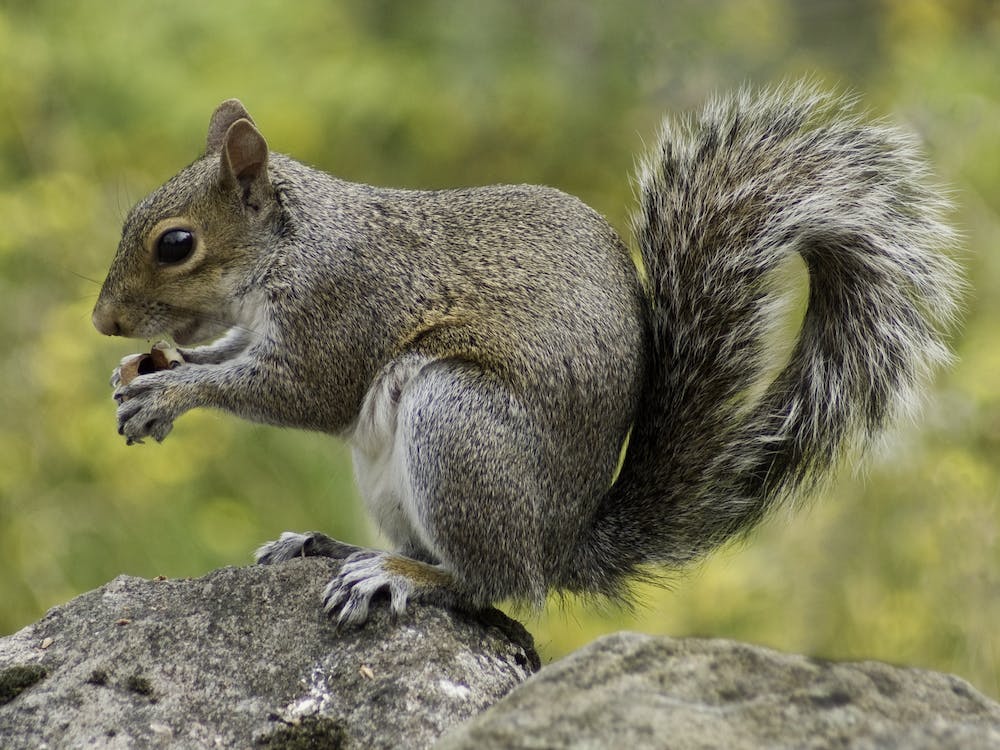
The Cape Ground Squirrel, also known as the South African Ground Squirrel and Xerus inauris, is a common squirrel species found in dry parts of southern Africa. This species belongs in the Sciuridae family with its closest relatives, including the tree squirrels, ground squirrels, chipmunks, flying squirrels, and prairie dogs.
The Cape Ground Squirrel was first described in 1780 by German geographer and zoologist Eberhardt August Wilhelm von Zimmermann. It was recognized that the name “Cape” associated with its common name is a little misleading because the species occupies a much larger area than the Cape provinces. However, researches still pushed through with this name to distinguish the species from the Eastern Grey Squirrel, a tree squirrel that was imported from Europe by Cecil John Rhodes to Cape Town in South Africa.
The general population of this species dos not appear threatened overall. Although in some regions, they are persecuted as pests to their agricultural livestock. Because they damage crops and are known carriers of rabies, humans have utilized poisonous grass to control their population and damage. Yet still, not all Cape Ground Squirrels are persecuted. Some Cape Ground Squirrels can be sighted in Kgalagadi Transfrontier Park in South Africa and Botswana and Etosha National Park in Namibia. For these reasons, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List categorized the Cape Ground Squirrels as Least Concern.
Its seven levels of scientific classification are as follows:
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Rodentia
Family: Sciuridae
Genus: Xerus
Species: X. inauris
The physical characteristics of a Cape Ground Squirrel
The Cape Ground Squirrel has a coarse, short hair. Its skin is black, and at the back of its body, it has either light or dark reddish-brown shade. Its underparts, limbs, neck, and face are white in color. They have adorable, short ears. One distinct characteristic is their long white tail that is as wide and long as their body.
Cape Ground Squirrels are sexually dimorphic. An adult male measures 435 to 476 mm and weighs 423 to 649 g, whereas an adult female measures around 435 to 446 mm and weighs between 444 to 600 g.
The distribution and habitat of Cape Ground Squirrels
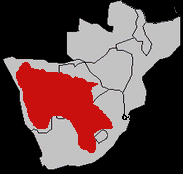
Cape Ground Squirrels are commonly found in southern Africa, particularly in Namibia, Botswana, and South Africa. They frequent tropical and dry areas such as savannahs and grasslands. They are abundant in the Kalahari Desert. They live in burrows, which shield them from the harmful effects of extreme weather conditions and predation.
The behavior of a Cape Ground Squirrel
This species is a diurnal mammal that leaves its burrow in the morning before sunrise to groom itself and bask in the sun. After this, it will start foraging in the grasslands. During the afternoon, it will groom or socialize with other squirrels. During the hottest hours of the day, it will raise its large, fluffy tail to give shade itself against the scorching heat. It shuttles during these hours—meaning it goes in and out of its burrow to regulate body temperature.
Female Cape Ground Squirrels are social animals that form groups of 1 to 4 females with their offspring. They share living quarters and often from each other. Male Cape Ground Squirrels live in a separate quarter, with groups that have 19 members each. Females do not have a social hierarchy, while males have a strict linear hierarchy that depends on age.
Mating season occurs all-year-round, though it mostly occurs during dry winter. Female Cape Ground Squirrels copulate with multiple males. After copulation, males will masturbate to clean their genitals and reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections. After a gestation period of 48 days, the female squirrel will give birth to a litter with 1-3 pups.
This squirrel species is a common prey of Black-backed Jackals. Cape Ground Squirrels use their olfactory cues to detect predators. When a predator is nearby, a male and female squirrel will “mob” attack it, which is characterized by putting their tails between their bodies and the predator’s body. This “mobbing attack” is only a form of defense. When a predator fully attacks, the Cape Ground Squirrels will run away or flee.
The diet of a Cape Ground Squirrel
Cape Ground Squirrels feed on grasses, herbs, seeds, shrubs, bulbs, and various insects.
WILDLIFE PARKS AND RESERVES WHERE THIS SPECIES IS FOUND: